Understanding Temperature, Heat Index, and Wet Bulb Globe Temperature

When we talk about the weather, temperature is often the first thing that comes to mind. But the temperature alone doesn’t give us a complete picture of the atmospheric conditions. To understand the comfort, safety, and potential weather phenomena, we also need to consider other terms like the “heat index” and the “wet bulb globe temperature”. Let’s dive into the differences between these terms and why they matter.
1. Temperature:
Definition: Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the molecules in a substance. In simpler terms, it tells us how hot or cold something is.
Why it matters: Temperature affects everything from our daily comfort to the operation of machinery. It plays a role in determining the state of water (solid, liquid, or gas) and influences weather patterns. For humans, extreme temperatures can be dangerous, leading to conditions like hypothermia or heatstroke.
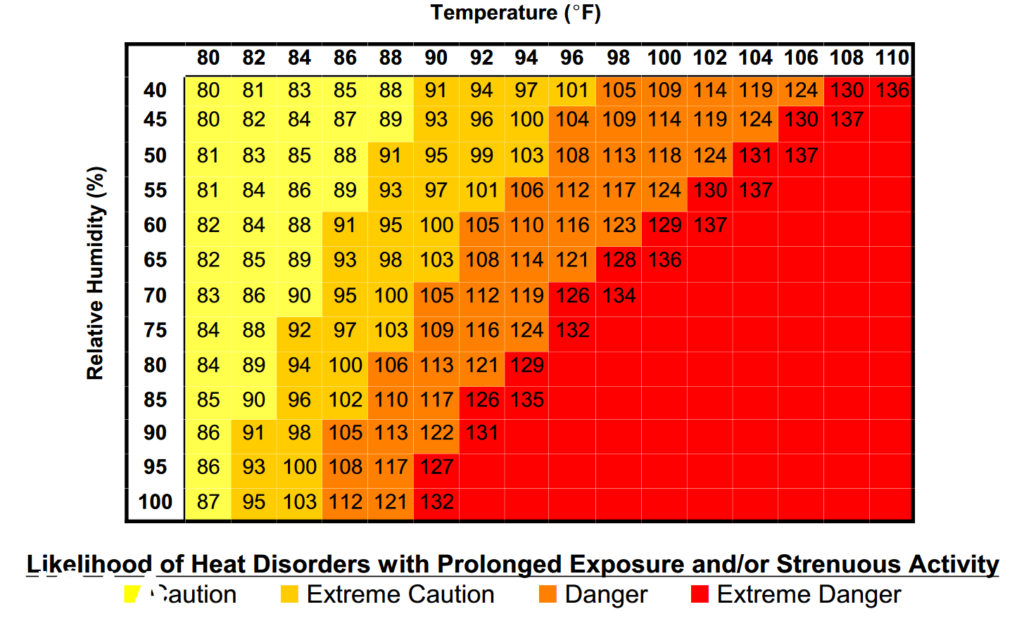
2. Heat Index
Definition: The heat index, sometimes referred to as the “apparent temperature,” is a measure that combines air temperature and relative humidity to determine how hot it feels to the human body. When humidity is high, our body’s ability to cool itself through sweating is reduced, making it feel hotter than the actual air temperature.
Why it matters: High heat index values can be dangerous. When the body can’t cool itself effectively, there’s a risk of heat-related illnesses like heat exhaustion or heat stroke. By paying attention to the heat index, individuals can take precautions like drinking more water, seeking shade, or avoiding strenuous activities during the hottest parts of the day. Learn more tips about heat safety when the temperatures spike to dangerous levels.
3. Wet Bulb Globe Temperature (WBGT):
Definition: WBGT is a composite temperature used to estimate the effect of temperature, humidity, wind speed, and solar radiation on humans. It’s derived from three temperature readings: wet bulb temperature (which considers moisture), dry bulb temperature (standard air temperature), and black globe temperature (which accounts for radiant heat).
Comparing WBGT and Heat Index
| WBGT | Heat Index | |
| Measured in the Sun |  |  |
| Measured in the Shade |  |  |
| Uses Temperature |  |  |
| Uses Relative Humidity |  |  |
| Uses Wind |  |  |
| Uses Cloud Cover |  |  |
| Uses Sun Angle |  |  |
Why it matters:
- Human Safety: WBGT is widely used to assess the risk of heat-related illnesses. For instance, sports organizations might use WBGT to decide if conditions are safe for athletes to compete without risking heat exhaustion or heat stroke.
- Occupational Health: Many industries use WBGT to determine safe working conditions and rest breaks for workers, especially in outdoor or non-air-conditioned environments.
- Military Training: Armed forces around the world use WBGT to ensure the safety of their personnel during training exercises.
Final Thoughts
While the standard temperature gives us a general idea of the day’s warmth or coldness, it doesn’t always tell the whole story. The heat index and WBGT provide more detailed insights into how we might actually experience the conditions, especially when humidity and direct sunlight come into play. By understanding and monitoring these metrics, we can make safer decisions for outdoor activities, protect vulnerable populations, and ensure that everyone can enjoy the summer months with minimal risk.
Thank you Zach